Intro to Single Cell RNA-Seq Workshop
UM Bioinformatics Core Workshop Team
Workshop goals and topics
By the end of the workshop, attendees will be able to
- Describe (at a high level) how sc samples are sequenced along with strengths of a few popular library preps.
- Create and interpret preliminary QC visualizations from a sc experiment.
- Use Seurat, PCA, and UMAP to create cell-type clusters and projections.
- Identify marker genes and annotate clusters based on gene expression.
- Execute and visualize differential expression across clusters.
This workshop is targeted toward researchers who would like to be able to run scRNA-Seq analysis independently. This workshop assumes some experience working with R/R-Studio. Basic understanding of NGS sequencing protocols and/or familiarity with bulk RNA-Seq analysis is desirable.
Please let us know if there is anything we can do to improve the workshop experience.
Our purpose is not to be exhaustive, there is a lot that we cannot cover in the allotted time, and we don’t expect anyone to be an expert at the end of the workshop. But we hope you will have a familiarity with key concepts, data types, tools, and how they all connect to one another in the service of a biological question.
About the workshop team
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chris | Marci | Raymond | Dana |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Weisheng | Ford | Tricia |
Code of Conduct
Be kind to others. Do not insult or put down others. Behave professionally. Remember that harassment and sexist, racist, or exclusionary jokes are not appropriate for the workshop.
All communication should be appropriate for a professional audience including people of many different backgrounds. Sexual language and imagery is not appropriate.
The Bioinformatics Core is dedicated to providing a harassment-free community for everyone, regardless of gender, sexual orientation, gender identity and expression, disability, physical appearance, body size, race, or religion. We do not tolerate harassment of participants in any form.
Thank you for helping make this a welcoming, friendly community for all.
If you have questions about the CoC please reach out to the hosts during the workshop, or email us at bioinformatics-workshops@umich.edu.
To report a CoC incident/concern, please email Chris Gates (Bioinformatics Core, Managing Director) at cgates@umich.edu or contact the University of Michigan Equity, Civil Rights, and Title IX Office at ecrtoffice@umich.edu.
Using Zoom and Slack
We will be recording this session. Recordings will be available to participants
following the workshop.To see what the instructor is sharing, click the “Chris’s Screen” button in the top of the Zoom window.
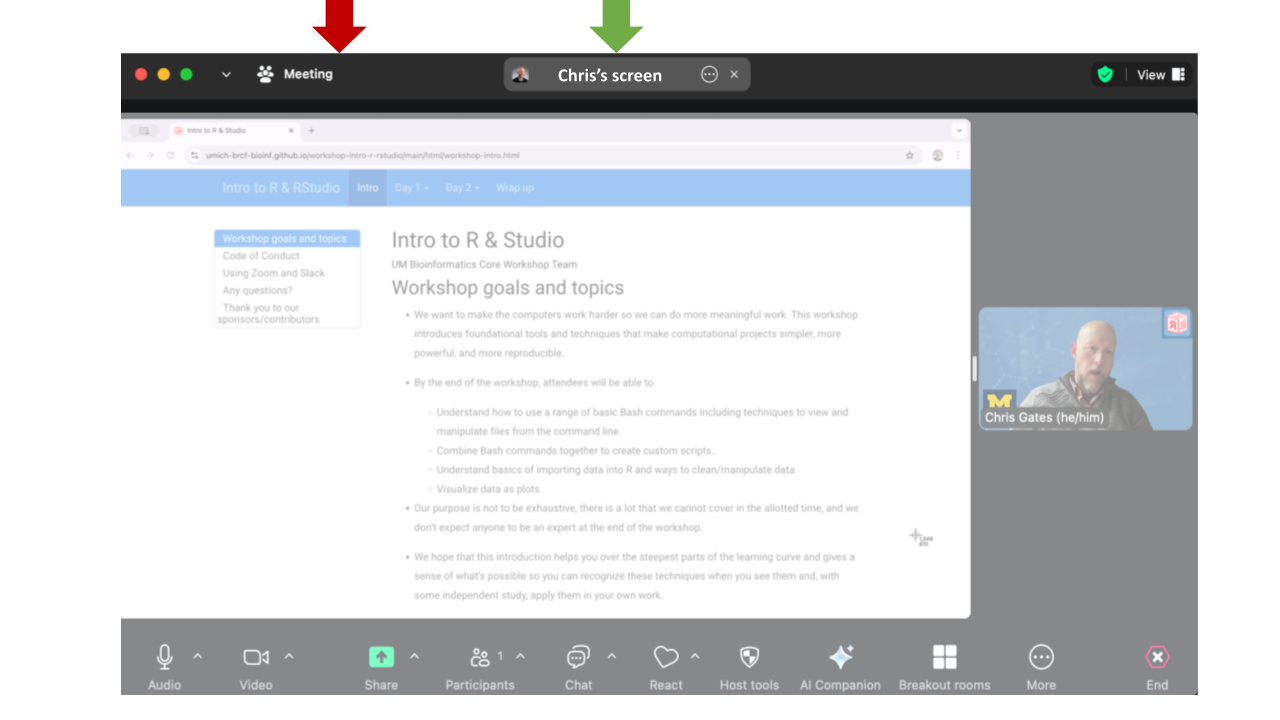
Zoom controls are at the bottom of the Zoom window:

To minimize distractions, we encourage participants to keep their audio muted (unless actively asking a question).
To maximize engagement, we encourage participants to keep their video on.
Slack works better than Zoom’s Chat function so avoid Zoom Chat for now.
You can enable transcription subtitles for your view.
We will be using Breakout Rooms occasionally for ad-hoc 1-1 helper support. We will review this in detail together in a few minutes.
Zoom’s “Reactions” are a useful way to interact. You can access these from the React button.
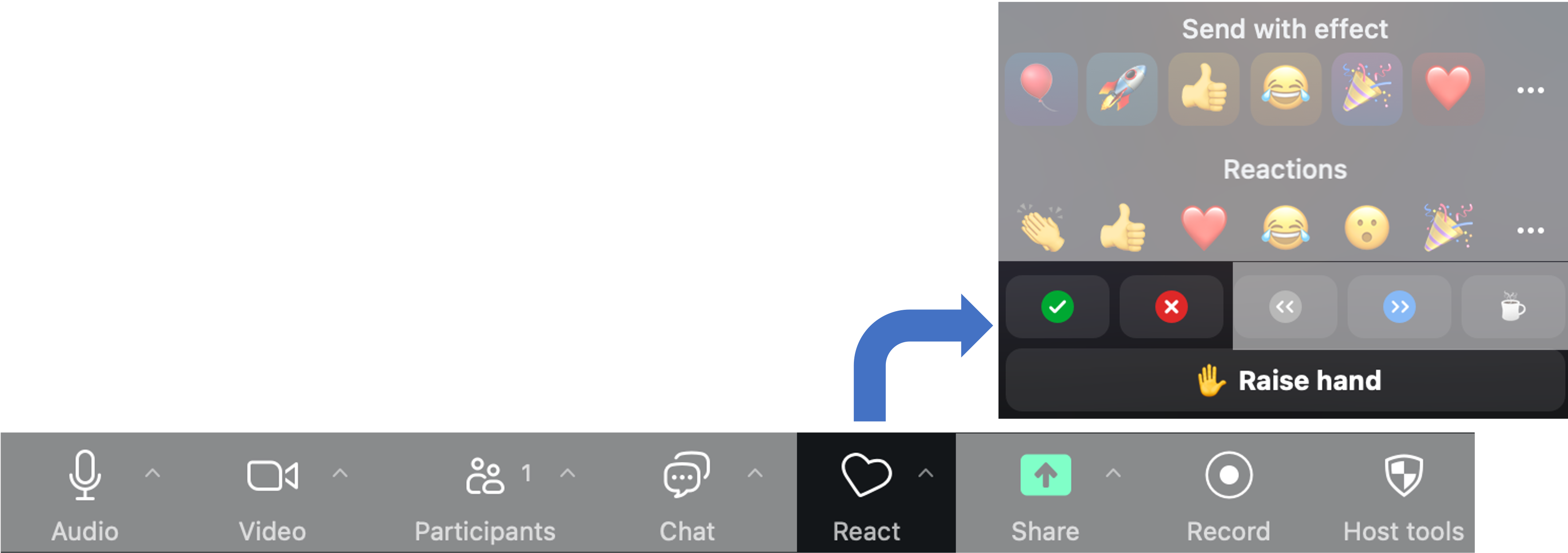
- Raise Hand to request clarification or ask a question. (Same an in-person workshop.)
- Instructors will use Green check and Red
X to poll the group at checkpoints along the way.
Exercise: Use Zoom non-verbals
- Everyone use Zoom to raise your hand.

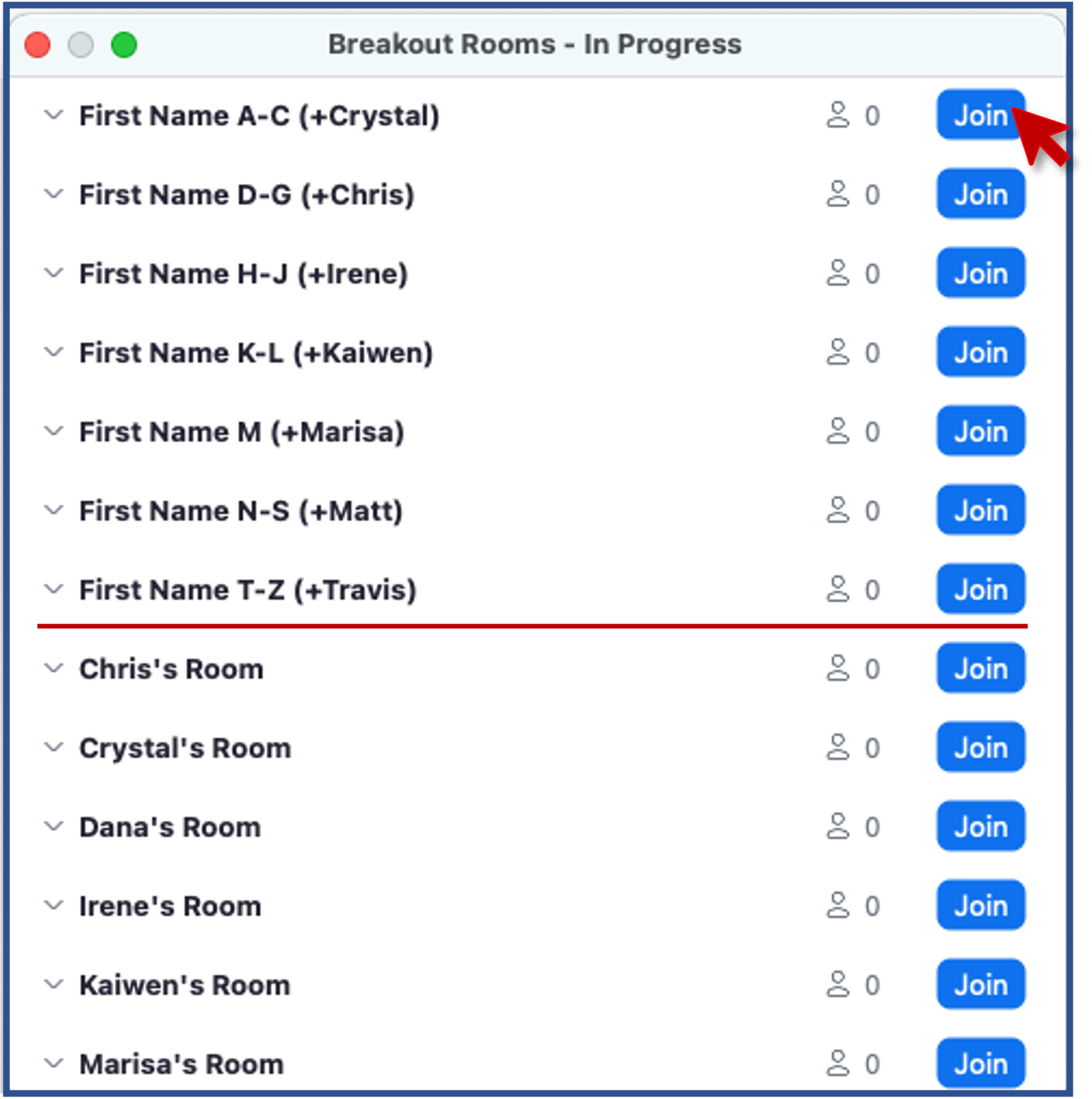
Exercise: Using Zoom Breakout Rooms
Take a moment to briefly introduce yourself (name, dept/lab, area of study) in a breakout room.
- Zoom: Click Breakout Rooms
- Find the room corresponding to the first letter of your first name
- Click Join button to the right of the room.
- When you have completed introductions, you can leave the breakout room to rejoin the main room.
- Slack can be used to communicate to the group or to individuals and has a few features/behaviors that we prefer over Zoom’s Chat functionality.
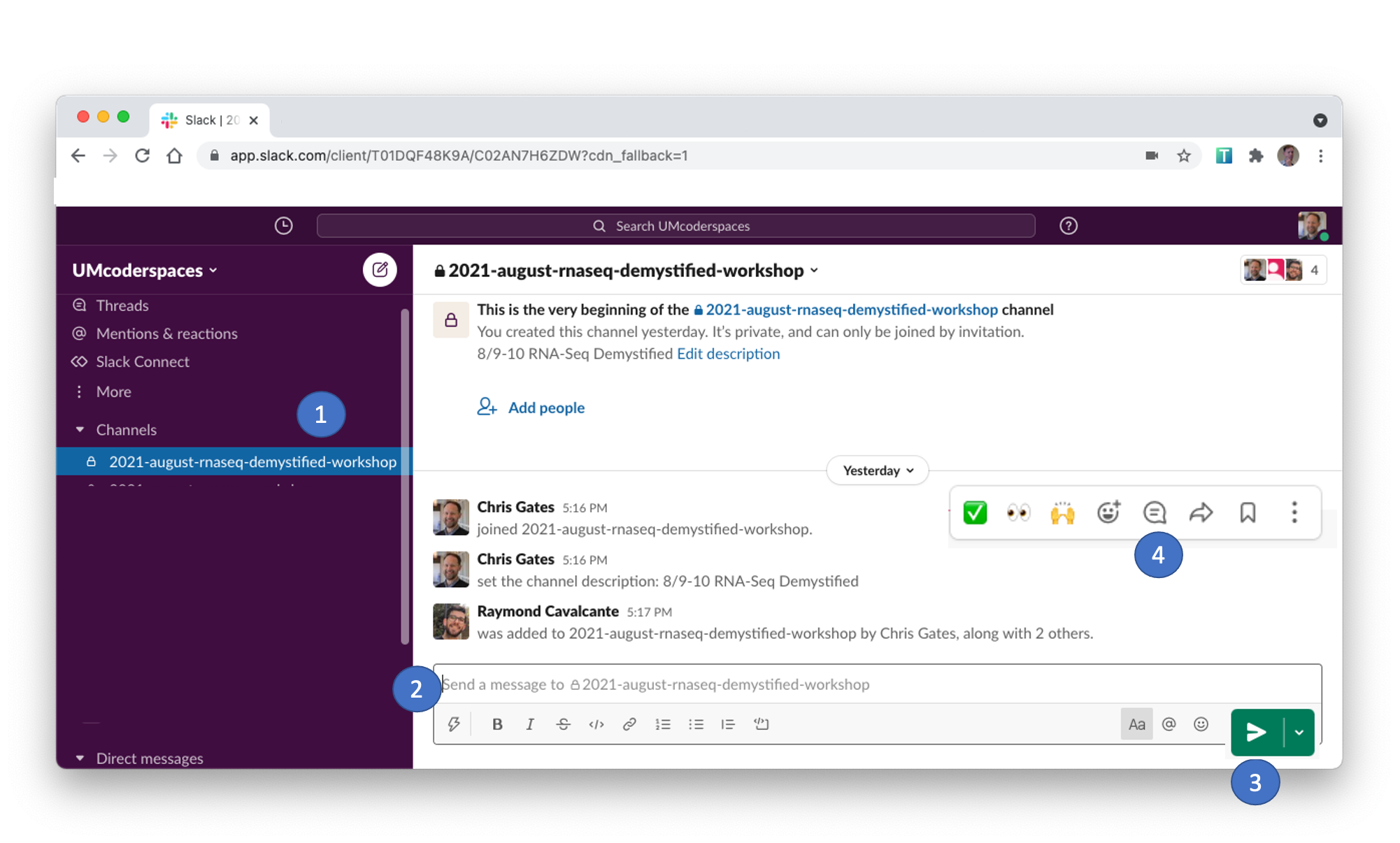
- Slack messages will be posted to the
2025-10-intro-single-cell channel.
Click on the channel in the left pane (1) to select this channel. - You can type in the message field (2); click send (3) to post your message to everyone.
- Helpers will respond in a Slack thread (or pose the question to the instructor)
- You can respond in a message thread by hovering over a message to trigger the message menu and clicking the speech bubble (4).
Exercise: Responding in Slack thread
In your scRNA-Seq experiment, what do/did you hope to find?
Review of Key communication patterns
 |
 |
|
|---|---|---|
| “I have an urgent question” |  |
Post a question |
| “I have a general question” | Post a question | |
| “I’m stuck / I need a hand” | Post a note | |
| Instructor check-in |  -or-
-or-  |
|
| Instructor Slack question | Respond in Slack thread |
Exercise: Group checkpoint
- Using Zoom, give me a green-check if you feel like
you understand communication patterns or red-X if you
need clarification.
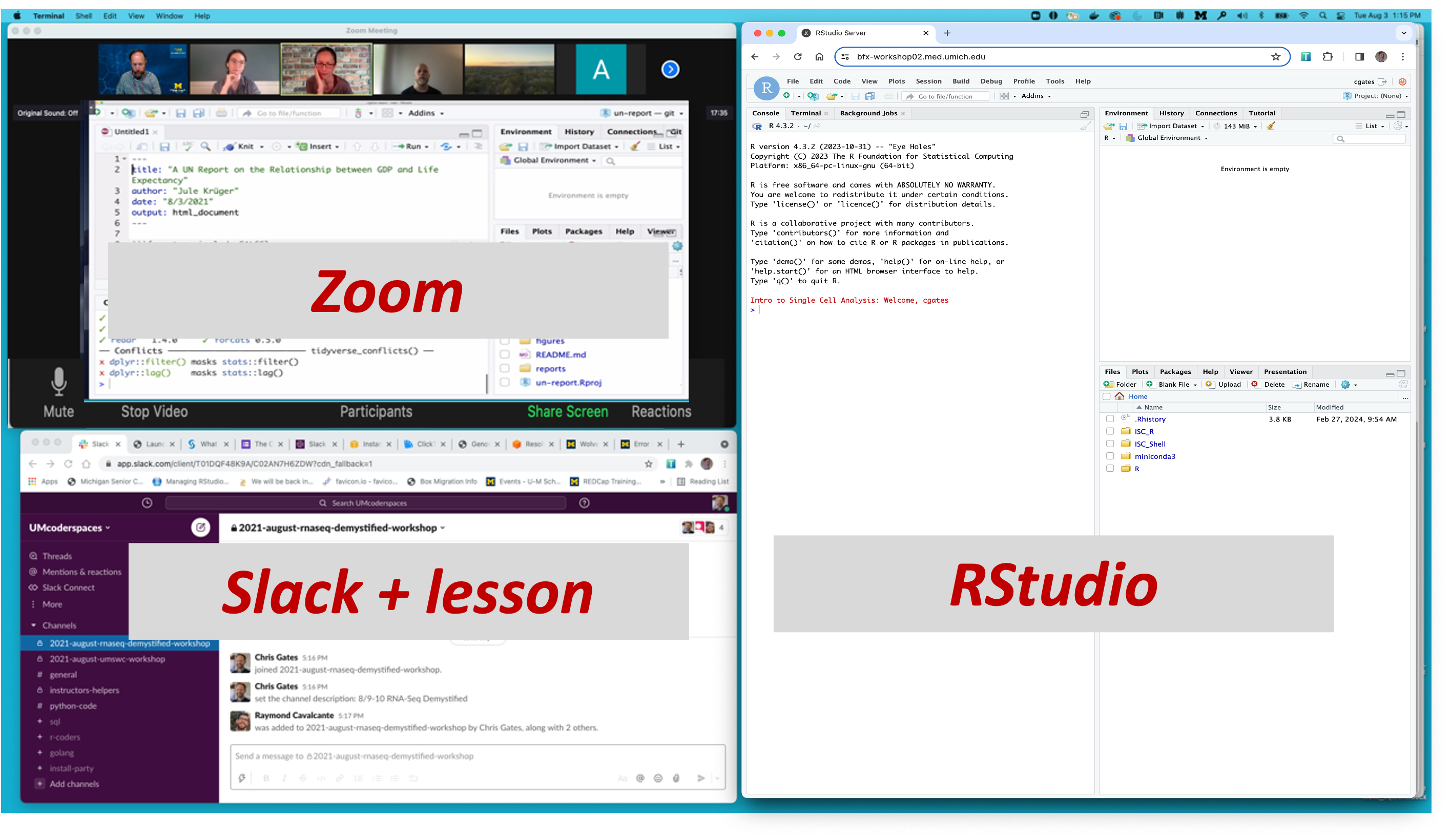
Arranging your screens
It is important that you can see:
- Zoom (instructor’s shared screen + reactions)
- Your R/Studio screen
- Slack
- Lesson plan web page
Any questions?
Thank you to our sponsors/contributors

UM BRCF Bioinformatics Core
- The University of Michigan BRCF Bioinformatics Core is a team of analysts that help researchers design, analyze, and interpret high-throughput genomics experiments.
- Last year we helped about 60 researchers design and execute about 100 projects including gene expression, epigenetic, variant identification, functional enrichment and many other kinds of analyses.
- We provide letters of support for grant proposals.
- We are creating a series of bioinformatics-focused workshops.
Biomedical Research Core Facilities
Biomedical Research Core Facilities (BRCF) helps researchers
economically take advantage of the latest technology and collaborate
with top experts in the field. Established in 1986, the BRCF was formed
to offer centralized access to research services and equipment.
University of Michigan Library
Our mission is to support, enhance, and collaborate in the instructional, research, and service activities of faculty, students, and staff, and contribute to the common good by collecting, organizing, preserving, communicating, sharing, and creating the record of human knowledge.
Acknowledgements
Sections of the workshop were extended/adapted from or inspired by sources below. These and other specific references are cited throughout the text and/or in the References section of each lesson.
The workshop Code of Conduct has been adapted the NumFocus Code of Conduct (https://numfocus.org/code-of-conduct) which itself draws from from numerous sources, including the Geek Feminism wiki, created by the Ada Initiative and other volunteers, which is under a Creative Commons Zero license, the Contributor Covenant version 1.2.0, the Bokeh Code of Conduct, the SciPy Code of Conduct, the Carpentries Code of Conduct, and the NeurIPS Code of Conduct.
Some icons/images were sourced from https://openclipart.org/.
These workshop lesson plans have been adapted and extended from materials listed above. These are open access materials distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.